The Role of Smart Thermostats in Modern Heating Systems
Smart Thermostats: The Brain of Modern Heating Systems
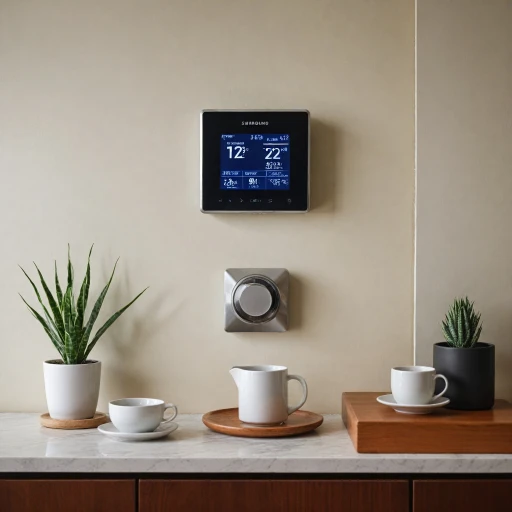
The introduction of smart thermostats as a pivotal component in contemporary heating systems has revolutionized the way homeowners manage indoor climates. Much like the brain governs the functioning of a body, a smart thermostat oversees the dynamics of your heating system, providing adjustments based on varying thermal demands.
Smart thermostats play an instrumental role in optimizing heat pump systems. These devices seamlessly integrate with the systems to offer enhanced control over heating modes and energy efficient management. Given that heat pumps operate by transferring heat either from outdoor air or other heat sources, a smart thermostat ensures optimal efficiency by managing the reversing valve and compressor activities.
- Adaptive Climate Control: Smart thermostats are programmed to fine-tune temperature settings through learning user preferences and integrating real-time data. This feature is particularly beneficial when controlling the indoor air temperature, whether in heating or cooling mode.
- Energy Savings: Managing heat pump operations through a smart thermostat can lead to significant energy savings. By efficiently coordinating the compressor and evaporator coil functions, smart thermostats reduce energy waste and ensure the pump absorbs heat effectively during the colder months or dissipates it efficiently in warmer conditions.
- Environmentally Friendly: With their ability to seamlessly toggle between heating and cooling modes, smart thermostats promote the use of energy sources with a lower carbon footprint, maximizing the heat energy derived from renewable sources like water or air.
All these features underscore the significance of a smart thermostat within modern heat pumps. Appropriately handling components such as the expansion valve and condenser coil, a smart thermostat guarantees that your heating cooling systems function optimally, ensuring the comfort and satisfaction of its users.
Key Components of a Heat Pump
Essential Components in Heat Pumps
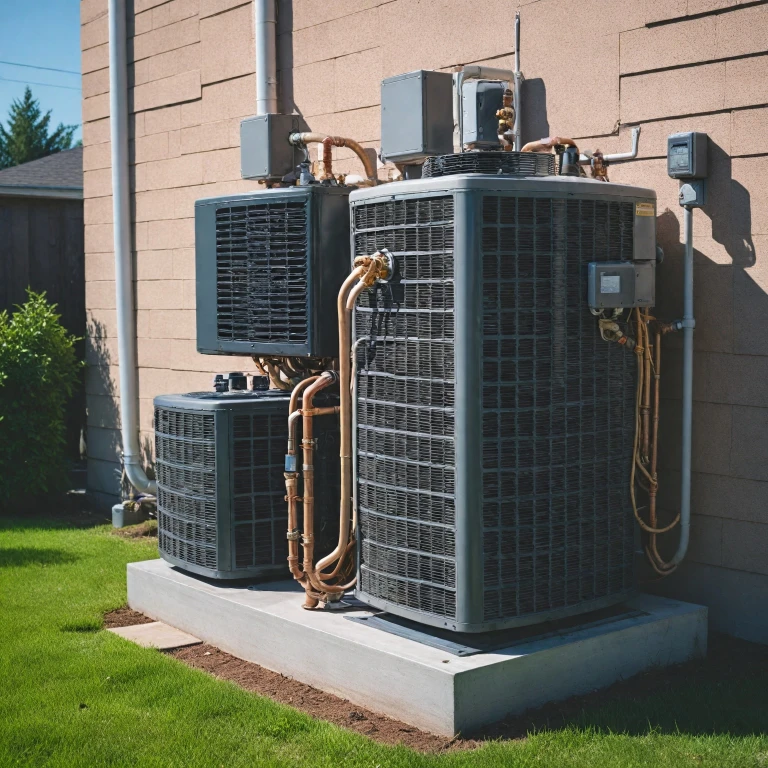
Heat pumps have become an integral part of modern heating and cooling systems due to their ability to transfer heat efficiently. They operate by absorbing heat from one area and releasing it in another, providing both heating and cooling solutions. Here’s a closer examination of their key components, crucial for optimizing energy efficiency:
- Compressor: The heart of the heat pump, responsible for pumping refrigerant through the system in a cycle. This enables the transfer of heat from the outdoor unit to the indoor air.
- Reversing Valve: This valve dictates the direction of the refrigerant flow, allowing the heat pump to switch between heating and cooling modes.
- Condenser Coil and Evaporator Coil: Both coils are essential for the heat exchange process. The condenser coil releases absorbed heat energy, while the evaporator coil absorbs heat from the source air.
- Expansion Valve: It regulates the refrigerant flow into the evaporator coil by reducing pressure, which helps in the absorption of heat.
- Outdoor Unit: Typically installed outdoors, it absorbs heat from the ambient outdoor air, especially in air-source heat pumps.
Understanding these components can significantly enhance the efficiency of your system, as the integration of a smart thermostat can further optimize their performance.
Integration of Smart Thermostats with Heat Pumps
Seamless Integration for Optimal Efficiency
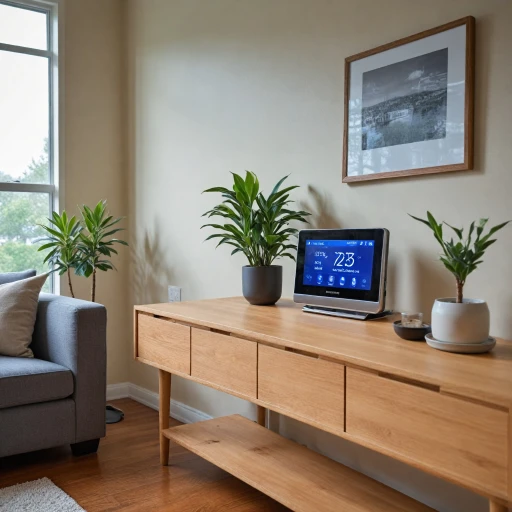
Integrating smart thermostats with heat pumps is a game-changer in modern heating and cooling systems. These devices work together to optimize energy use and enhance comfort. A smart thermostat acts as the brain of the system, communicating with the heat pump to adjust settings based on real-time data and user preferences.
Communication Between Devices
The integration process involves establishing a communication link between the smart thermostat and the heat pump. This connection allows the thermostat to send commands to the heat pump, such as switching between heating and cooling modes. For instance, when the thermostat detects a drop in indoor air temperature, it signals the heat pump to absorb heat from the outdoor air and transfer it indoors.
Advanced Features for Enhanced Control
Smart thermostats come equipped with advanced features that enhance the functionality of heat pumps. These include learning algorithms that predict user behavior and adjust settings accordingly. Additionally, they can manage the reversing valve in the heat pump, ensuring efficient switching between heating and cooling modes. The thermostat can also control the expansion valve, optimizing the flow of refrigerant through the evaporator coil and condenser coil.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
By integrating with heat pumps, smart thermostats help maximize energy efficiency. They adjust the compressor speed and manage the operation of the outdoor unit to minimize energy consumption. This not only reduces utility bills but also extends the lifespan of the pump system. For more detailed guidance on how smart thermostats enhance efficiency, you can explore this comprehensive guide.
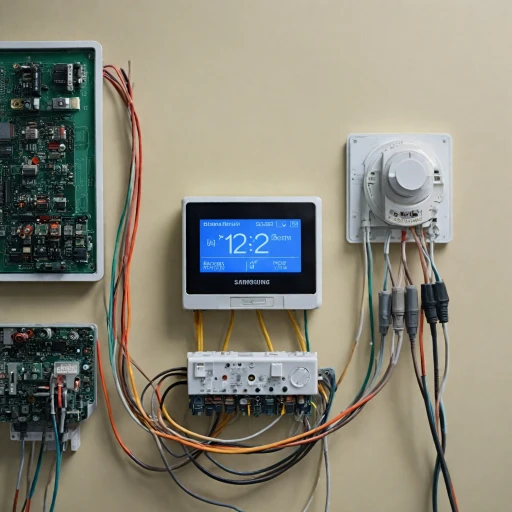
Compatibility and Installation Considerations
When integrating a smart thermostat with a heat pump, compatibility is crucial. Not all thermostats are designed to work with every type of heat pump system. It's essential to ensure that the thermostat supports the specific features of your heat pump, such as mini split systems or air source heat pumps. Proper installation is also key to achieving optimal performance, requiring attention to wiring and configuration settings.
Benefits of Using Smart Thermostats with Heat Pumps
Enhancing Efficiency and Comfort
Incorporating smart thermostats in conjunction with heat pump systems offers notable advantages to improve both efficiency and user comfort. With the integration of sophisticated sensor technology and intelligent algorithms, these devices allow users to precisely control the heating and cooling processes.- Optimized Performance: The smart thermostat continuously monitors the indoor air temperature and adjusts the heat pump's operation to ensure an optimal balance between energy consumption and comfort. This results in many homes achieving reductions in energy usage, as the heat pumps operate only when necessary.
- Seamless Transition: Smart thermostats excel in facilitating a smooth shift between heating and cooling modes. When the air source heat pump absorbs heat or switches to cooling mode, the thermostat coordinates with the pump system to guarantee smooth transitions. This adjustment reduces strain on the compressor and optimizes the use of heat energy.
- User-Friendly Interface: Many smart thermostats provide a user-friendly interface, often accessible via smartphones or other smart devices. This allows individuals to remotely manage their heating and cooling preferences, ensuring home environments are comfortable upon arrival.
- Improved Maintenance: By aggregating data from the heat pump's various components, such as the condenser and evaporator coils, smart thermostats can alert users to potential issues. This proactive approach enables timely maintenance, often preventing costly repairs.
Challenges in Smart Thermostat and Heat Pump Integration
Overcoming Integration Hurdles
Integrating smart thermostats with heat pumps presents its own set of challenges. One significant hurdle is ensuring compatibility between different thermostat models and the varied types of heat pumps, such as air source heat pumps or mini split systems. Each system has specific requirements, and not all smart thermostats are designed to handle these differences effectively. In heat pump technology, elements like the reversing valve and expansion valve play essential roles in switching between heating and cooling modes. The thermostat must accurately control these components to avoid operational inefficiencies. Problems can arise if the smart thermostat fails to correctly signal the heat pump system when to switch modes, which could lead to decreased energy efficiency or discomfort in maintaining indoor air temperatures. Another challenge involves the heat pump's compressor and outdoor unit. During cooling mode, the evaporator coil absorbs heat from indoor air, while in heating mode, it requires precise coordination to transfer heat energy into the home. A mismatch in thermostat settings or programming errors can disrupt this delicate balance, potentially resulting in high energy consumption or system damage. Moreover, integrating smart thermostats with heat pump systems requires comprehensive user understanding. Many homeowners are unfamiliar with advanced settings, such as those involving the refrigerant cycle and how to best optimize system energy efficiency. This knowledge gap can hinder effective utilization of the smart thermostat's capabilities, emphasizing the need for user-friendly interfaces and informative resources. In solving these challenges, manufacturers and developers must focus on creating more universally compatible devices and providing comprehensive guidance. As the technology evolves, these efforts will be crucial in maximizing the potential of smart thermostat and heat pump integration.Future Trends in Smart Thermostat and Heat Pump Technology
Emerging Technologies Shaping Smart Thermostats and Heat Pumps
As we venture further into the era of smart technology, it becomes intriguing to see how advancements will shape the future of smart thermostats and heat pumps. Highlighted below are some cutting-edge trends and technology shifts that are likely to redefine this domain, optimizing both heating and cooling systems.- AI-Powered Energy Management: Integration of advanced AI technologies is set to revolutionize how smart thermostats and heat pump systems function. Through machine learning, these systems can anticipate user preferences, optimize cooling and heating operations, and even adjust settings autonomously to ensure energy efficiency.
- Enhanced Connectivity: The continuous growth of the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable more seamless connectivity among heat pump systems and smart thermostats. This interconnectedness promises improved synchronization between the pump system and thermostat, optimizing the transfer of heat and thereby reducing energy consumption.
- Efficient Heat Exchange Technology: Developments in heat exchange technologies are focusing on more efficient ways to use refrigerants, evaporator coils, condenser coils, and compressors. Aspects like improved expansion valves and reversing valves are targeted to boost the performance of both cooling mode and heating mode.
- Focus on Renewable Energy Sources: With an increasing emphasis on sustainable and eco-friendly solutions, air source heat pumps that harness renewable energy are becoming prevalent. Innovations in solar-assisted heat pump units are leading the charge in providing carbon-neutral heating and cooling solutions.
- Advanced Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics, future systems can more accurately predict the heating energy demands of a home by analyzing patterns of indoor air and outdoor air temperatures. This ability to dynamically adapt will make heating and cooling systems more user-centric and efficient.
- Smart Zoning and Room-Specific Control: As mini split systems become more sophisticated, they will allow for enhanced control of individual rooms through smart thermostats, ensuring that specific spaces receive customized heating or cooling without unnecessarily consuming energy across the entire house.